Carotid Artery Stenosis Ultrasound Diagnosis
September 11, 2020
DVT: Deep Venous Thrombosis
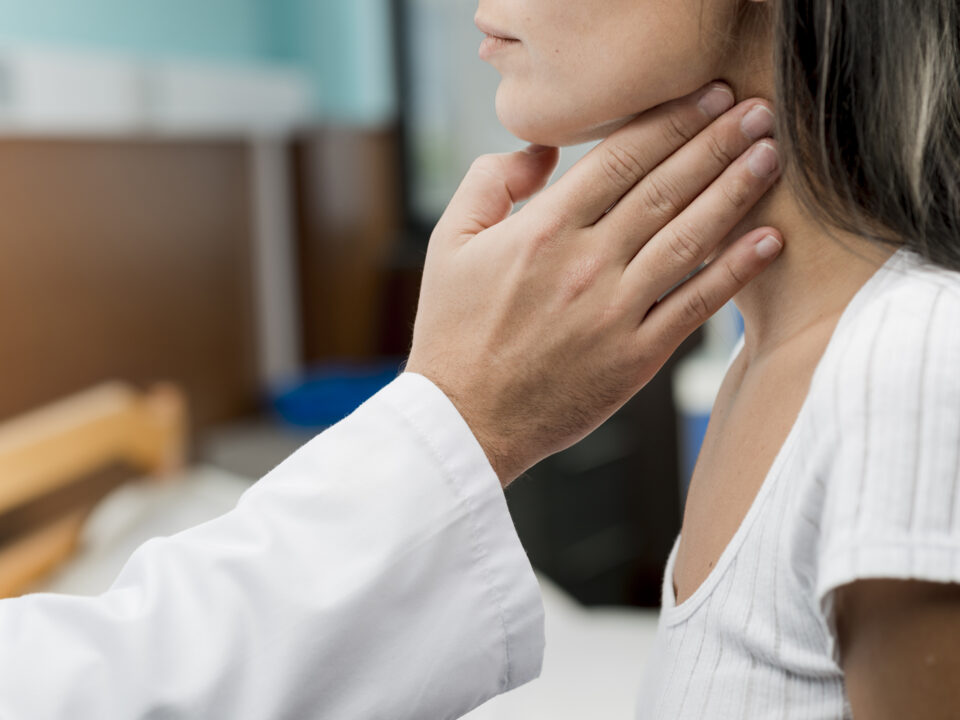
September 13, 2020A Biopsy is a sample of tissue taken from the body to look at it more closely. It is recommended when a first test suggests an area of tissue in the body is abnormal.
An Ultrasound-guided Biopsy is an image-guided procedure that uses ultrasound technology to help Specialist Radiologists perform needle biopsies.
Which ultrasound scanner is the best for ultrasound-guided Biopsy purposes?
The Specialist Radiologist uses the ultrasound to locate and guide a specialized needle to the correct area of the body. The needle is then used to collect a tissue sample before being carefully removed from the body.
Our SONOSOF’s Research and Development team always recommend the Mini Linear Handheld WiFi Ultrasound Scanner MLCD to radiologists, surgeons, and Doctors of Osteopathy, which is built with a needle guide that provides more accurate needle placement in all the body joints.
The Mini-Linear WiFi Ultrasound Scanner MLCD has an Electronic array scan mode with a B, B/M display, high frequency from 10MHz to 14MHz, advanced digital imaging technology which provides a superior image quality (12f/s), and most importantly it is small light and easy to carry(250g).
An advantage of Mini-Linear WiFi Ultrasound Scanner MLCD guided procedures is the control of the needle insertion path with 20-55mm depth and, if needed, the possibility to modify the needle depth or angle without the risk of damaging adjacent structures. Moreover, it helps the practitioner locate a lump or abnormality and remove a tissue sample for examination under a microscope.
Ultrasound is used to detect changes in the appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels and to detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
The goal of a biopsy is to remove a sample of tissue for testing in a laboratory. A biopsy can help diagnose abnormalities such as benign and malignant thyroid tumors. During the biopsy, an imaging physician will use the ultrasound scanner to accurately guide a needle to the site of the biopsy. The needle will then be used to remove a tissue sample.
If a surgical biopsy is being performed, ultrasound may be used to guide a wire directly into the targeted finding to help the surgeon locate the area for excision( a type of surgical biopsy in which an entire lesion or abnormal group of cells and tissue, as well as a surrounding margin of normal-appearing tissue, are removed).
With continuous ultrasound imaging, the physician is able to view the biopsy needle or wire as it advances to the location of the lesion in real-time.
References: Biopsy , Ultrasound_guided Biopsy