Ultrasound Scanner for Bladder Diverticulum
September 24, 2020
Breast Masses
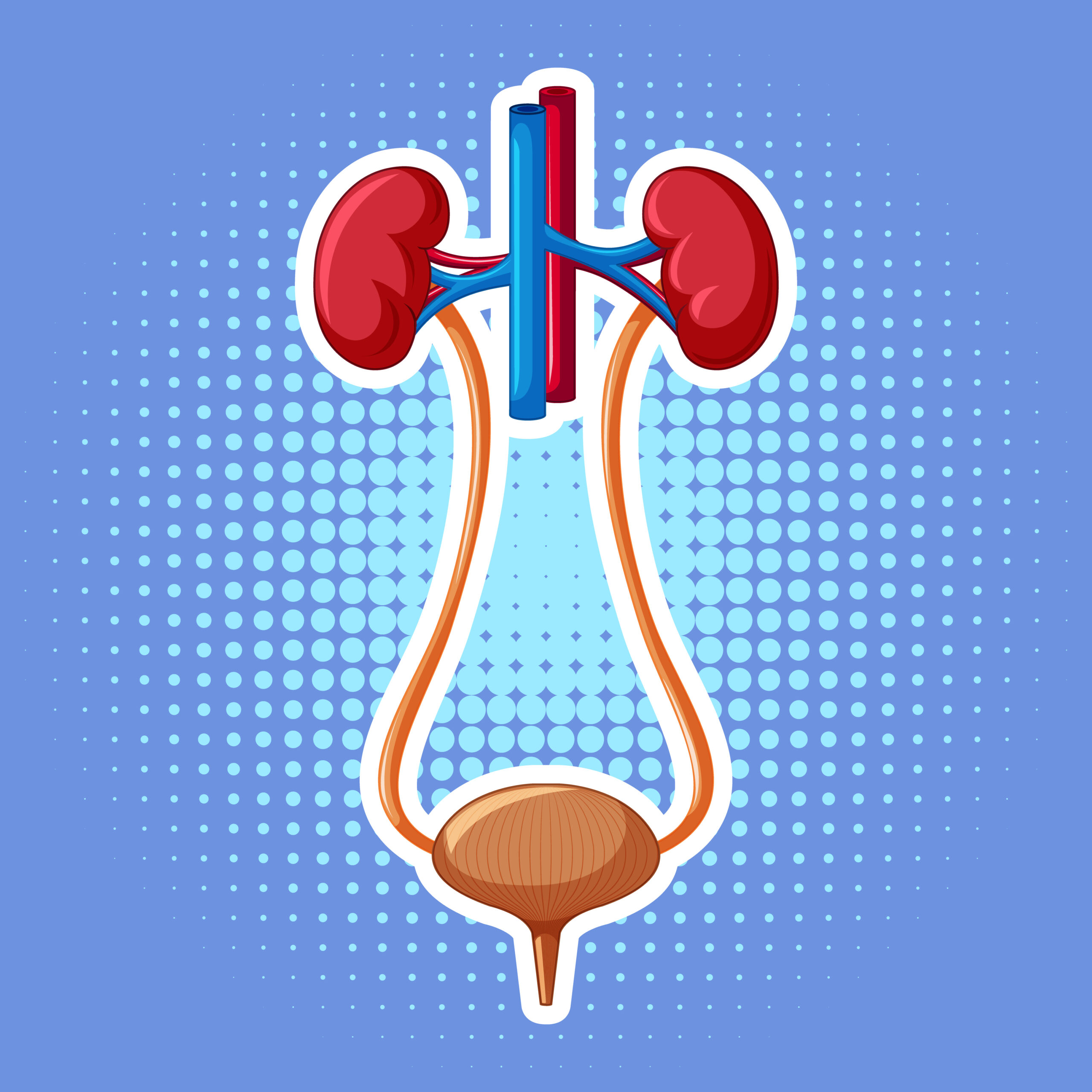
September 27, 2020Kidney ultrasound is also known as renal ultrasound, is a painless noninvasive exam that uses ultrasound waves to produce images of the kidney.
It is used to assess the size, location, and shape of the kidneys and related structures such as the arteries and bladder. Moreover, it can detect cysts, tumors, abscesses, and infection within or around the kidneys, etc…
Which ultrasound Scanner is best for Kidneys diagnosis ?
Generally speaking, the kidneys can be examined during either normal respiration or breath hold, as they will follow the diaphragm and change position accordingly.
Yet, in the adult patient, a curved array transducer with frequency of 3.5 MHz is used. While the pediatric patient should be examined with a linear array transducer with higher center frequencies. Based upon this, our SONOSIF ‘s Research and Development team always recommends the Convex and Linear Color Doppler Wi-Fi Double head Ultrasound Scanner CLCD to our urologists, nephrologists, and radiologists clients.
Artifacts of the lowest ribs always shadow the upper poles of the kidneys.
A kidney Ultrasound may be performed to assist in placement of needles used to Biopsy(obtain a tissue sample) the kidneys, to drain fluid from a cyst or abscess, or to place a drainage tube. This procedure may be used to determine blood flow to the kidneys through the renal arteries and veins. It may also be used after a kidney transplant to evaluate the transplanted kidney.
A renal ultrasound may be performed on an outpatient basis or as a part of your stay in a hospital. Usually, the ultrasound procedure follows this process:
* Drinking 3 eight-ounce glasses of water at least one hour before the exam and not emptying the bladder.
* Removing clothing and jewelry since you’ll likely be given a medical gown.
* Lying face-down on an exam table.
* Having a conductive gel applied to the skin in the area being examined.
* Having the transducer rubbed against the area being examined.
* The sound will be reflected off structures inside the body, and the ultrasound machine will analyze the information from the sound waves.
* The ultrasound machine will create images of these structures on a monitor. These images will be stored digitally.
Furthermore, the renal ultrasound exam does not need any preparation of the patient and it is generally performed with the patient in the supine position. The kidneys are examined in longitudinal and transverse scan planes with the transducer placed in flanks.
At the point when insonation of the kidney is obscured by intestinal air, the supine scan position is combined with the lateral decubitus position with the transducer moved dorsally. Preferably, the exam is initiated in the longitudinal, parallel to the long diameter of the kidney, as the kidney is easier to distinguish.
References: Ultrasonography of the kidney , Kidney Ultrasound , Renal ultrasound.