- Immediate contact :
- +1-323-988-5889
- info@sonosif.com

Venous Ultrasound: VU
October 13, 2020
VeniPuncture: VP
October 15, 2020An abscess is a painful collection of pus, usually caused by a bacterial infection. Abscesses can develop anywhere in the body.
A small skin abscess may drain naturally, or simply shrink, dry up and disappear without any treatment.
However, larger abscesses may need to be treated with antibiotics to clear the infection, and the pus may need to be drained. This will usually be done either by inserting a needle through The skin or by making a small incision in the skin over the abscess. Preferably, using an Ultrasound to identify its location.
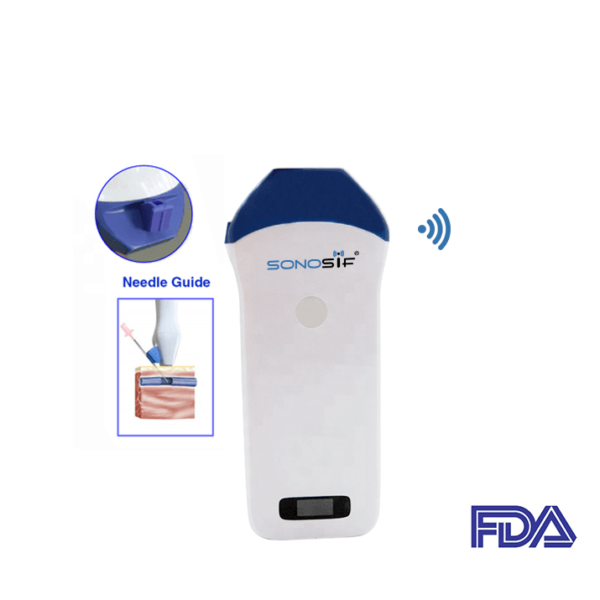
Which Ultrasound Scanner is used for Abscesses imaging?
Using the high-frequency 10 to 14 MHz Mini-Linear Handheld Wi-Fi Ultrasound Scanner MLCD is highly needed for Abscesses assessment and the identification of the location.
Most abscesses are adequately and safely drained by catheter, Catheter drainage has the advantages of avoidance of general anesthesia. Ultrasonography has become the preferred method of detecting abdominal abscesses and also of guiding percutaneous catheter drainage.
Real-time sonography has the advantages of being inexpensive, “portable,” and able to provide simultaneous imaging during catheter placement. Moreover, it provides greater accuracy in guiding drainage of small, deep abscesses, more accurate delineation of the extent and location of the collection, and better definition of the relationship of abscesses to bowel and blood vessels.
Ultrasound can characterize the size and depth of an abscess and can be used to directly guide incision and drainage. Furthermore, it can be used at the bedside and presents no risk to the patient.
To sum up, ultrasound devices are valuable diagnostic tools. To help with decision-making and improves clinicians’ ability to differentiate between cellulitis and abscess and, thus, to initiate the most appropriate treatment from the outset.