- Immediate contact :
- +1-323-988-5889
- info@sonosif.com

Acupuncture: Evaluating the biomechanical effects of needle manipulation on tissue
October 27, 2020
PICC: Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
October 27, 2020Pulmonary aspiration of gastric content is a major anesthetic-related complication which may result in significant morbidity and mortality. This is particularly true in high-risk patients and situations such as parturient, emergency surgery, and diseases associated with slow gastric emptying.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive portable tool that assesses gastric content and volume to clinically evaluate aspiration risk by providing qualitative and quantitative information.
The main objective of point-of-care (POC) gastric ultrasound is to help clinicians assess gastric contents when NPO status, which is unknown or uncertain in the immediate pre-anesthetic period.
Which Ultrasound Scanner is suitable for Gastric evaluation?
The Convex and Linear Color Doppler Wi-Fi Double Head Ultrasound Scanner CLCD is highly suggested to our Gastroenterologists, anesthesiologist, emergency physicians, and intensivists clients.
This Device has two heads. Thus, making it more practical and more affordable than buying two separate single-headed probes. The Linear side of the Doppler allows you to evaluate the more superficial parts of the body while the Convex part is used for in-depth examinations.
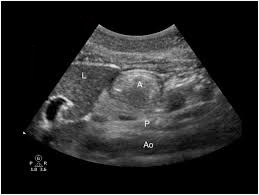
A curved array low-frequency transducer (2–5 MHz) with standard abdominal settings is most useful in adults. It provides the necessary penetration to identify the relevant anatomic landmarks.
A linear high-frequency transducer can be used in leaner or pediatric patients or to obtain detailed images of the gastric wall. The gastric wall is 4–6 mm thick and has a characteristic appearance of five distinct sonographic layers that are best visualized with a high-frequency transducer (e.g. 5–12 MHz) in the fasting state.
Gastric ultrasound can help clinicians individualize aspiration risk at the bedside and more appropriately guide anesthetic management.
Furthermore, Gastric US can provide valuable insight into the nature and volume of gastric content before performing a block with sedation or inducing anesthesia for an urgent or emergent procedure where NPO status is unknown.
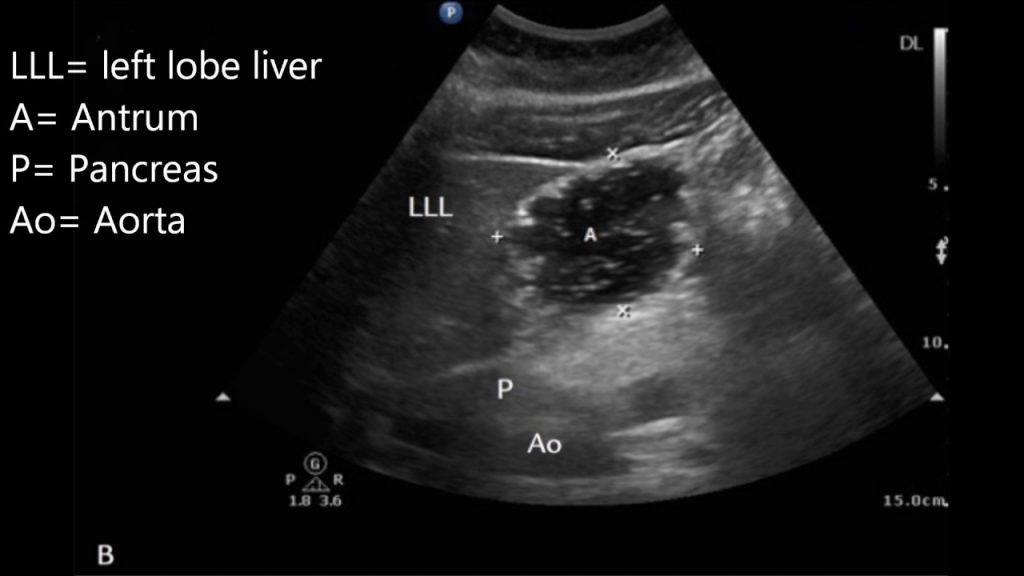
References: Ultrasound assessment of gastric content and volume, Gastric Ultrasound,
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SONOSIF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.