- Immediate contact :
- +1-323-988-5889
- info@sonosif.com

The Use of Ultrasound in Hospice and Palliative Care
February 5, 2022
Ultrasound-Guided Coxofemoral Joint
February 14, 2022Nerves are delicate and can be harmed by pressure, stretching, or severing. A nerve injury can disrupt signals to and from the brain, causing muscles to malfunction and a loss of feeling in the injured area.
The following are some symptoms of nerve damage:
Numbness or tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
Feel as if you’re wearing a glove or sock.
Muscle weakness, particularly in the arms or legs.
Dropping objects you’re holding on a regular basis.
Sharp aches and pains in your hands, arms, legs, or feet.
A buzzing sensation similar to a mild electrical shock.
An ultrasound scan is one method for diagnosing nerve damage.
Nerve function examinations.
Electromyography (EMG) detects nerve damage by recording electrical activity in your muscles.
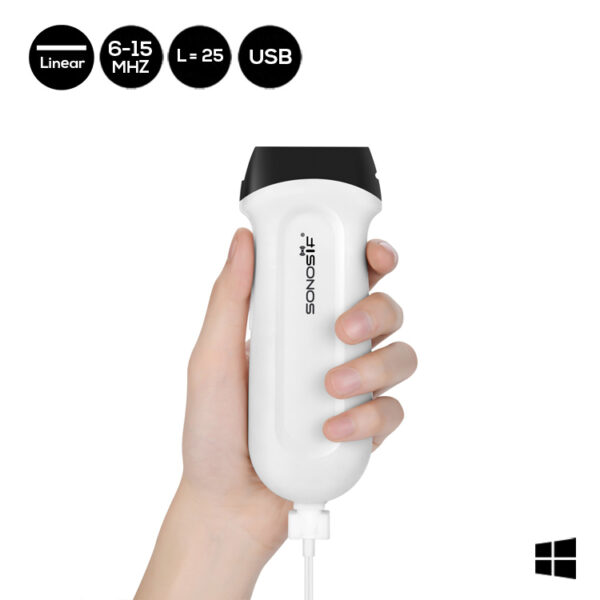
The USB-UL3 Linear 6-15MHz Ultrasound Scanner is a scanning device that can perform electromyography.
It has a wide range of applications, including Vascular, Thyroid, Breast, Musculoskeletal, Lung, and, of course, Nerve, making it extremely effective in the field of neurology.
The device also has a simple USB connection, which helps to improve point-of-care, clinical diagnostic methods, and clinic diagnosis efficiency.
Furthermore, because of the USB-UL3 ‘s innovative features, such as being a waterproof device with a sealed head, it provides a steady ultrasound signal, which speeds up the signal transmission. As a result, the device produces incredible image quality, guiding Neurologists to a clear decision.
Another great feature of the machine is the USB model, which allows the health care provider to print or share images in seconds and share them with colleagues and even patients from your handheld ultrasound via email or network.
Such technological adaptability will undoubtedly ensure a more transparent form of diagnosis, with faster results and better treatment.
To summarize, the Ultrasound Scanner USB-UL3 appears to be an appropriate device capable of improving the quality of nerve ultrasonography and thus ensuring an accurate diagnosis as well as a quick and effective treatment.
Reference: Nerve Injuries