Ultrasound-Guided Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
October 18, 2020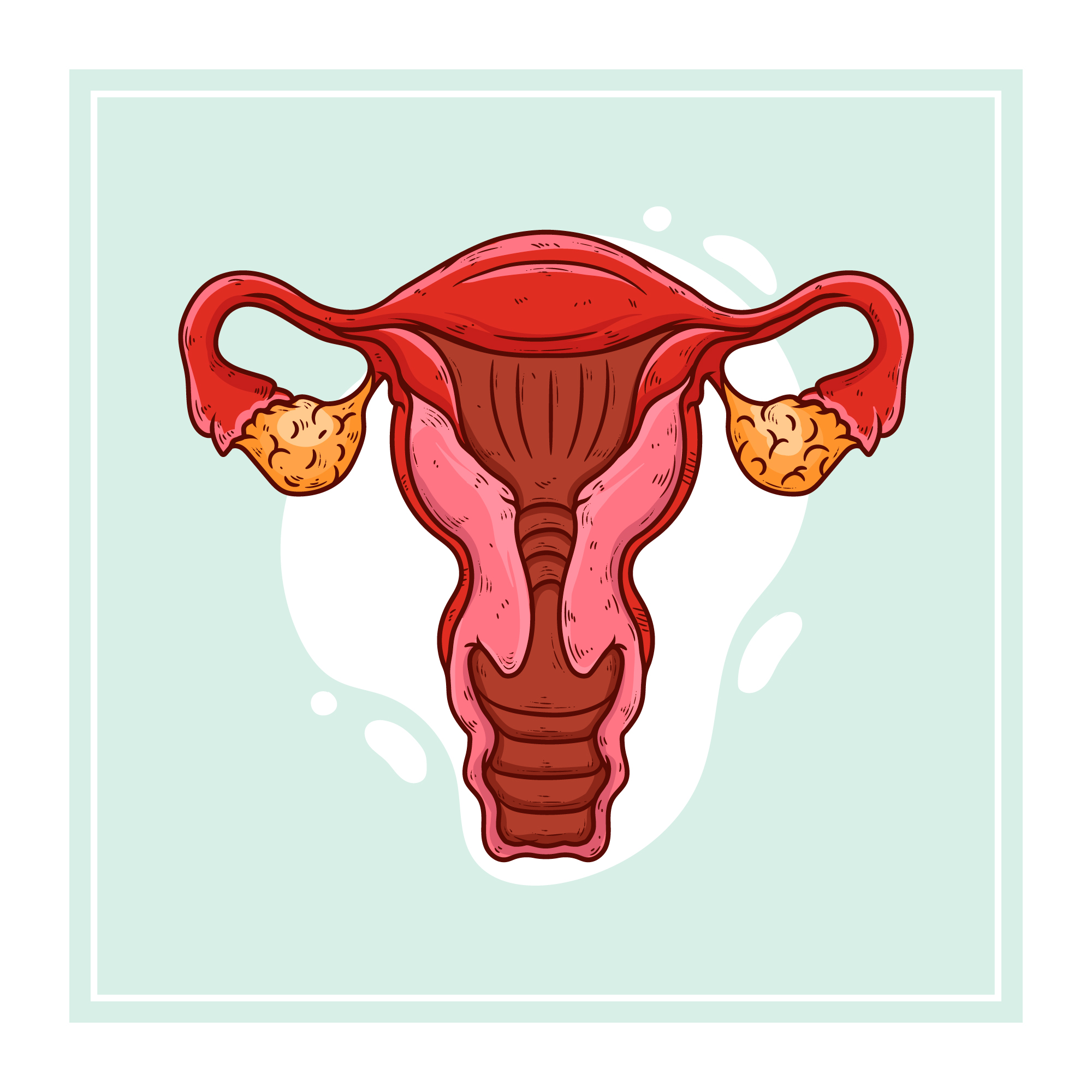
Abdominal Pelvic Scan
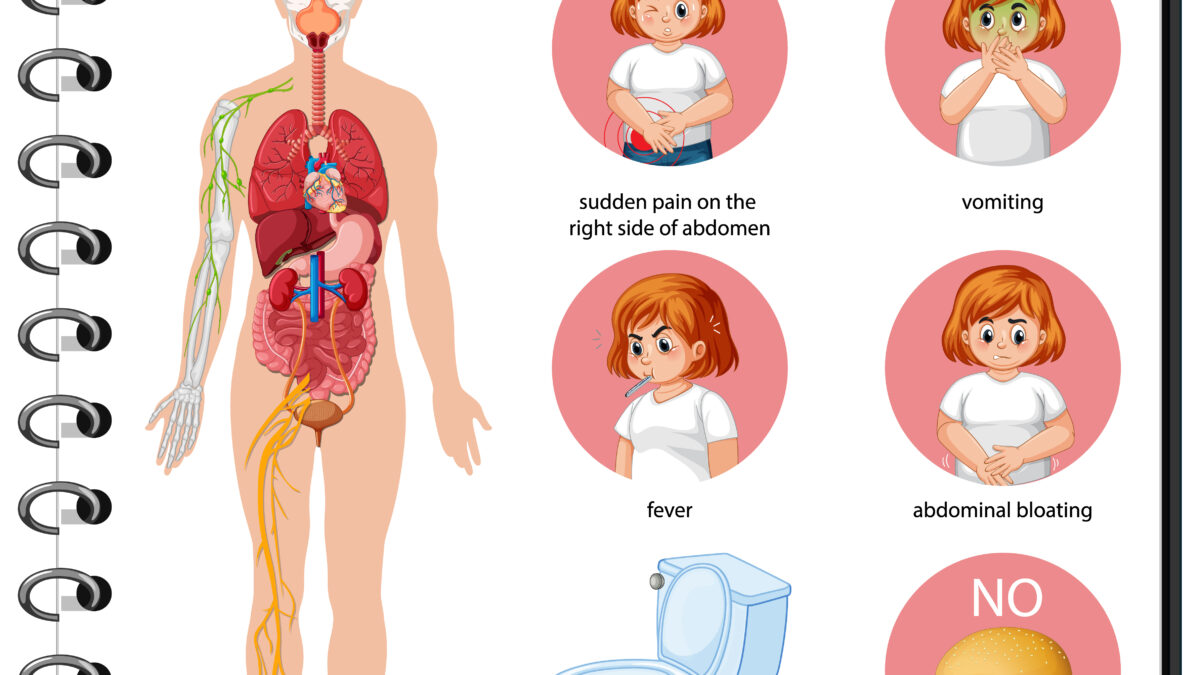
October 20, 2020Abnormal Appendix is an inflammation of the appendix, which is a finger-shaped pouch that projects from the colon on the lower right side of the abdomen.
Appendicitis causes pain in the lower right abdomen. However, in most people, pain begins around the navel and then moves. As the inflammation worsens, appendicitis pain typically increases and eventually becomes severe.
A blockage in the lining of the appendix that results in infection is the likely cause of appendicitis. The bacteria multiply rapidly, causing the appendix to become inflamed, swollen, and filled with pus. If not treated promptly, the appendix can rupture.
Which Ultrasound Scanner is best for Appendicitis assessment?
The Convex and Linear Color Doppler WiFi Double Head Ultrasound Scanner CLCD is highly recommended for Appendicitis assessment. In which, The Linear side of the Doppler allows you to evaluate the more superficial parts of the body while the Convex part is used for in-depth examinations.
Ultrasound can identify an enlarged appendix or an abscess. Nevertheless, during appendicitis, an enlarged inflamed appendix or abscess can be seen in 50% of patients. Ultrasound also is helpful in women because it can exclude the presence of conditions involving the ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and uterus (pelvic inflammatory disease, PID) that can mimic appendicitis.
The grayscale Ultrasound Scanner should be the first primary evaluation for patients suspicious of acute appendicitis, and color Doppler is an additional modality to increase sensitivity and more accuracy.
Knowledge of ultrasonographic findings of the normal and abnormal appendix helps reduce the time and effort involved in detecting normal appendix and to diagnose or exclude acute appendicitis confidently.
A study of the Value of sonography in detecting Appendicitis has shown that a normal appendix can be visualized in a high percentage of cases and it may present with an outer diameter > 6 mm (the widely-accepted upper limit of normal) due to the inspissated fecal material within the lumen. A significant percentage of early appendicitis can resolve spontaneously, especially when confined to the appendiceal tip.
A person with appendicitis may be seen first by family practitioners, internists, and pediatricians. However, usually, the person is evaluated by a general or another type of surgeon. Once appendicitis is suspected, a general surgeon always is consulted in case surgery is necessary.
Reference: Appendicitis, Sonography in the Evaluation of Acute Appendicitis
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SONOSIF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.