Ultrasound Scanner for Abnormal Enlargement of the Spleen
April 7, 2022
Ultrasound-Guided Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
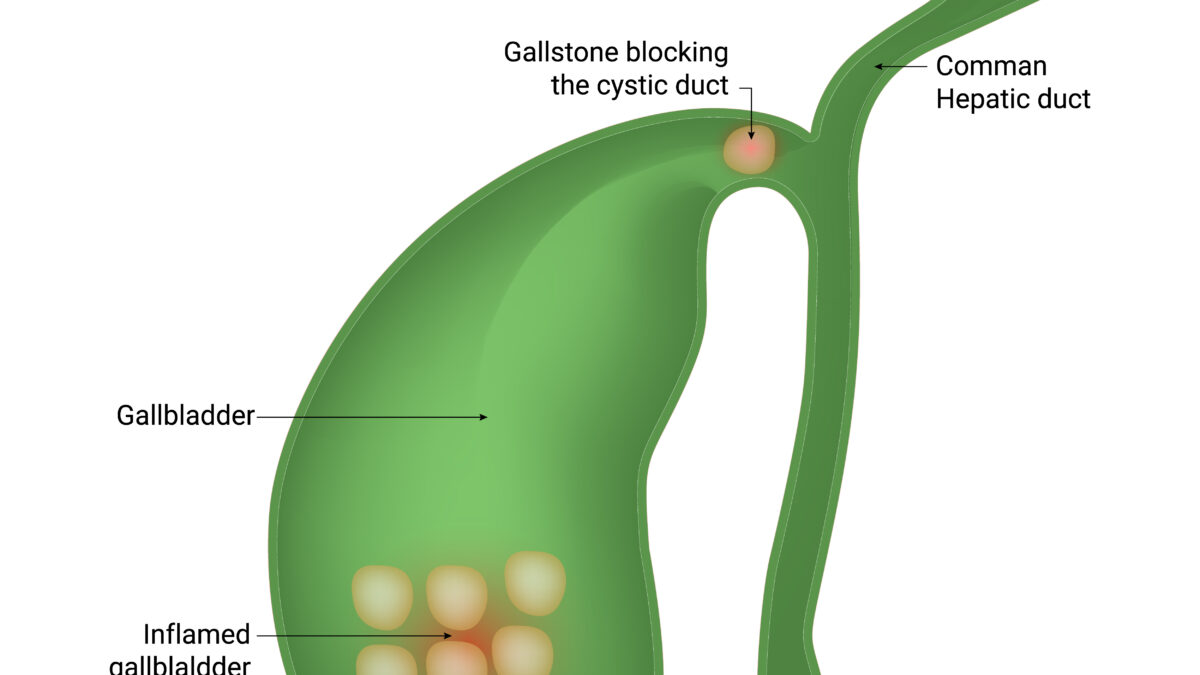
April 7, 2022Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver.
Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time.
It’s not clear what causes gallstones to form. Doctors think gallstones may result when:
· Your bile contains too much cholesterol. Normally, your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver excretes more cholesterol than your bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into crystals and eventually into stones.
· Your bile contains too much bilirubin. Bilirubin is a chemical that’s produced when your body breaks down red blood cells. Certain conditions cause your liver to make too much bilirubin, including liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections and certain blood disorders. The excess bilirubin contributes to gallstone formation.
· Your gallbladder doesn’t empty correctly. If your gallbladder doesn’t empty completely or often enough, bile may become very concentrated, contributing to the formation of gallstones.
Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the resulting signs and symptoms may include:
· Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen
· Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen, just below your breastbone
· Back pain between your shoulder blades
· Pain in your right shoulder
· Nausea or vomiting
People who experience symptoms from their gallstones usually require gallbladder removal surgery. Gallstones that don’t cause any signs and symptoms typically don’t need treatment.
However, in case of gallstones showed sole signs, treatment is a must, however, it should, of course, be preceded by a very meticulous diagnosis.
Ultrasound is the best imaging test for finding gallstones. In which the transducer bounces safe, painless sound waves off your organs to create an image or picture of their structure. If you have gallstones, they will be seen in the image.
Choosing a professional and the effective scanning device is what seems a bit tricky in this regard. For this reason, our medical-technical team designed an innovative scanning machine that seems perfect for the diagnosis of such an issue.
To meet the ultrasound parameters necessary for this specific ultrasonography procedure, a high-resolution Convex and Linear Color Doppler wireless Double Head Ultrasound Scanner CLCD is needed. The CLCD is the most typical device needed in this case.
This revolutionary color wireless ultrasound scanner has two heads, thus, making it more practical and more affordable than buying two separate single-headed probes.
The convex side of the color doppler transducer is used for in-depth examinations of the internal parts of the body and so it is convenient for examining Gallstones.
Accordingly, the Ultrasound Probe CLCD is specifically designed for gastroenterologists to produce colored Gallstones images and transfer them to your phone or tablet’s screen.
The device is IOS and Android compatible. Small and light, easy to carry, and easy to operate. As such, The CLCD does not compensate for the colored image quality.
With all these advanced functionalities combined, the FDA Color Double Head Wireless Ultrasound Scanner CLCD should be gastroenterologist and Gallstones patients’ first choice especially since it is specifically designed to observe major organs such as the liver pancreas and gallbladder too.
As such, patients shouldn’t worry since they’re going to be provided with accurate scan imagery and so safer examination.
Herein we highly recommend the FDA approved Convex and Linear Color Doppler wireless Double Head Ultrasound Scanner CLCD for Gallstones patients.
Reference:Gallstones
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SONOSIF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.