Platelet-Rich Plasma: PRP
October 18, 2020
Stellate Ganglion Block: SGB
October 18, 2020Facet joints are paired joints on the side of the midline at each level of the spine. A facet nerve block is a procedure in which a needle is placed into the facet joint under imaging guidance for the nerve root block injection of a local anesthetic and/or steroid.
A facet joint injection may be performed at one or multiple levels and on one or both sides (right/left) of the spine.
An ultrasound-guided facet nerve block is performed by physicians on patients with chronic back pain by facet arthropathy.
Which Ultrasound Scanner is suitable for Ultrasound-Guided Facet Nerve Block?
The Wireless Color Doppler Convex Ultrasound Scanner CC-3.1 allows physicians to obtain longitudianl facet views to identify the different spinal segments. Thanks to its high-resolution image and high-depth range of 100 mm to 200 mm, it allows the practitioner to accurately confirm the surface landmarks of the spinous process and iliac crest line.
It is strongly suggested to our radiologist and rehabilitation physician clients.
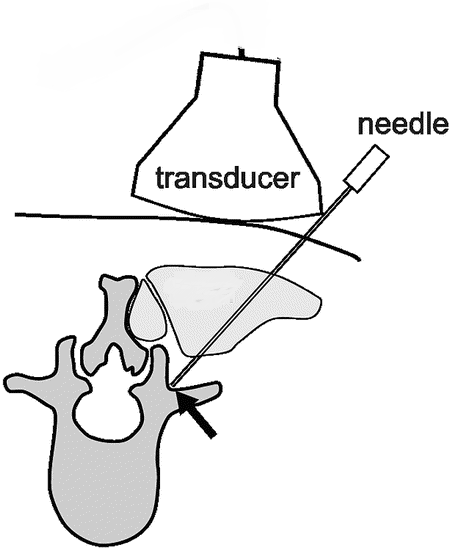
Ultrasound guidance is useful in facilitating peripheral and neuraxial blocks and offers direct visualization of the target, adjacent structures, and local anesthetic spread.
Ultrasound-guided injection provides similar efficacy as fluoroscopic guidance but provides benefits of zero radiation and real-time imaging.
The advantages of ultrasound guidance include but are not limited to increased success, decreased rates of complications, faster onset of blocks, and reduced amount of local anesthetics. Ultrasound measurements can even result in suggestions to modify established block techniques.
References: Ultrasound-guided Lumbar Facet Nerve Block, The Validation of Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Facet Nerve Blocks,