Ultrasound-Guided Suprapatellar recess
April 29, 2021
Superficial and Deep Infrapatellar bursa
May 6, 2021A bursa is a thin, slick sac-like film containing a small volume of fluid. A bursa is a soft tissue that is located between bones and soft tissues in and near joints. It supports and cushions joint surfaces, preventing them from rubbing against one another. Bursitis occurs as a bursa gets inflamed and irritated.
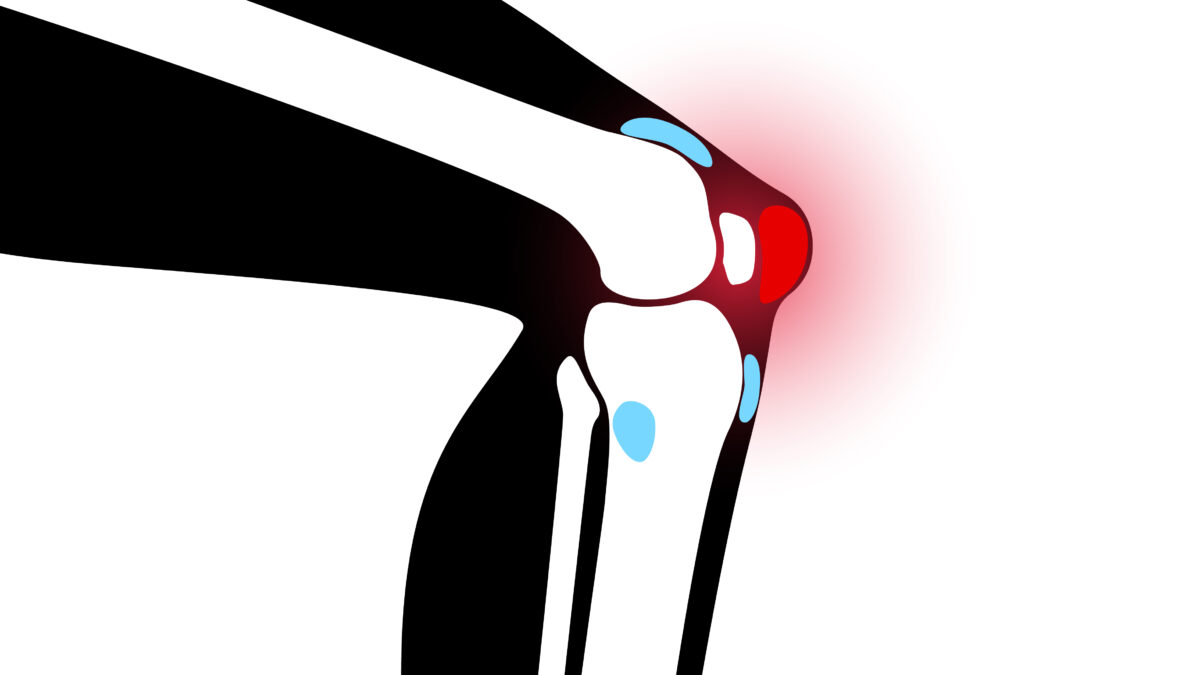
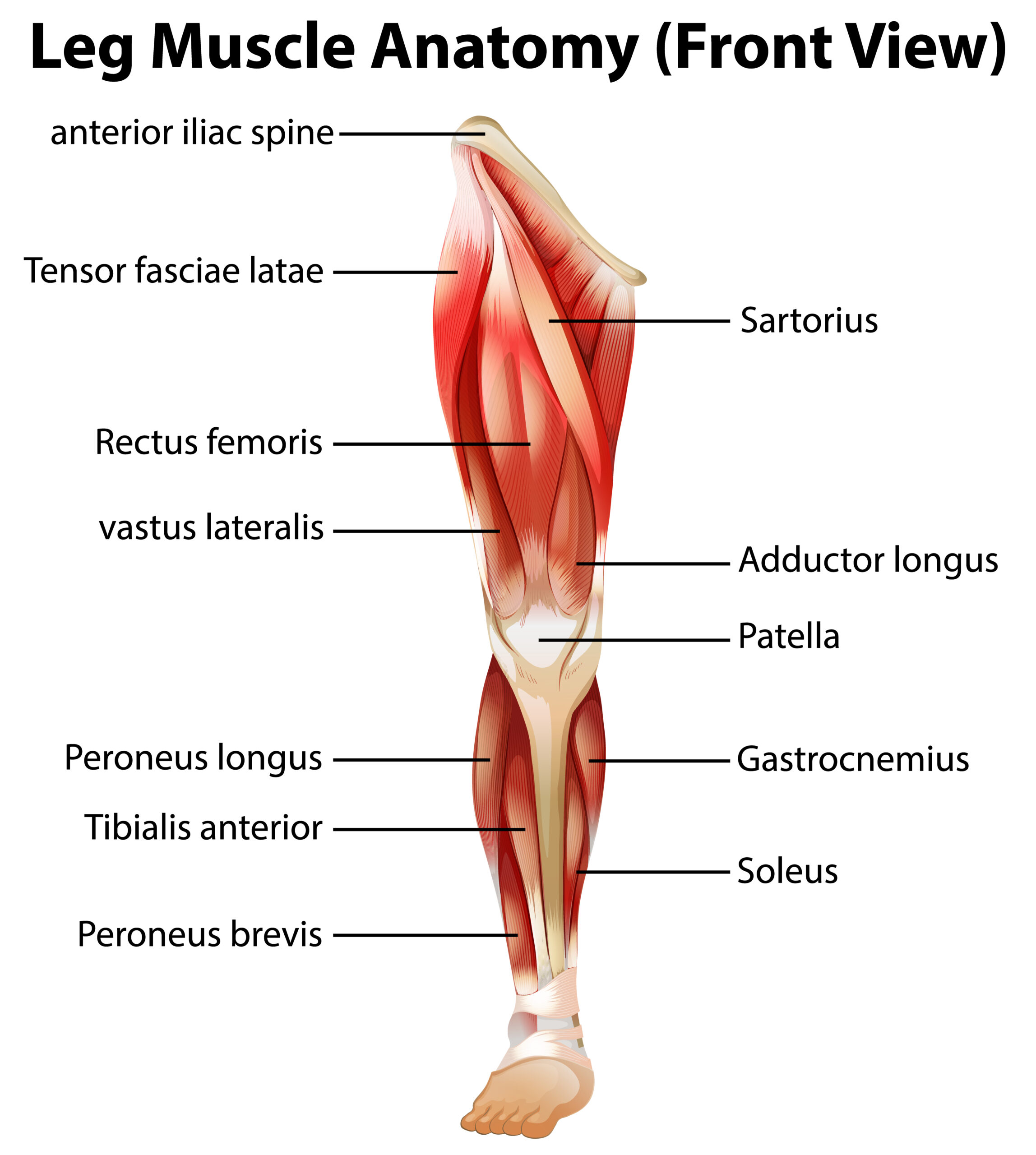
The Anserine bursa or pes anserine bursa is found on the inside of the knee joint. It lies between the shinbone (tibia) and 3 tendons that attach the hamstring muscles to the shinbone. Inflammation of this bursa is called pes anserine bursitis.
Ultrasound may reveal changes in the anserine bursa and saphenous nerve with great precision. It may be a useful tool for facilitating medical and rehabilitation approaches to the medial knee.
Which Ultrasound Scanner is the best for Anserine bursa diagnosis?
The use of a high-frequency ultrasound scanner is important for assessing the anserine bursa. This is an important step toward improving the precision and effectiveness of neuraxial and peripheral nerve blockades, as well as joint injection accuracy and effectiveness, by lowering the complication rate and improving our anatomical understanding.
For this reason, our medical research and development team highly recommends either the Color Doppler WiFi Linear Ultrasound Scanner 4-12 MHz CDC-2 or the Wireless Mini-Linear Color Doppler Ultrasound Scanner ML2CD to our orthopedist clients
CDC-2 has a frequency of 4-12 MHz, offer the ability to diagnose and treat patients sooner and with more accuracy.
It also has a higher production power since it offers a complete therapeutic solution. It features a simpler preset service, 32/64 physical channels, a self-developed algorithmic platform, and 32 per-point emissions and focuses for physicians. In addition, it has a Wi-Fi portable link as well as remote diagnosis and education capabilities.
On the other hand, ML2CD allows medical professionals to control the depth and assess the depth of the needle. It can be used to help diagnose and treat the medial portion of the knee as a valuable and quick tool.
Ultrasound is particularly receptive and precise when the inflammation is determined. This will help predict how long it takes for the patient to resolve and whether an ultrasonic injection is necessary or not.
References: Accuracy and efficacy of ultrasound-guided pes anserinus bursa injection, Pes Anserinus Bursitis, Sonoanatomic Variation of Pes Anserine Bursa, Understanding Pes Anserine Bursitis
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SONOSIF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.