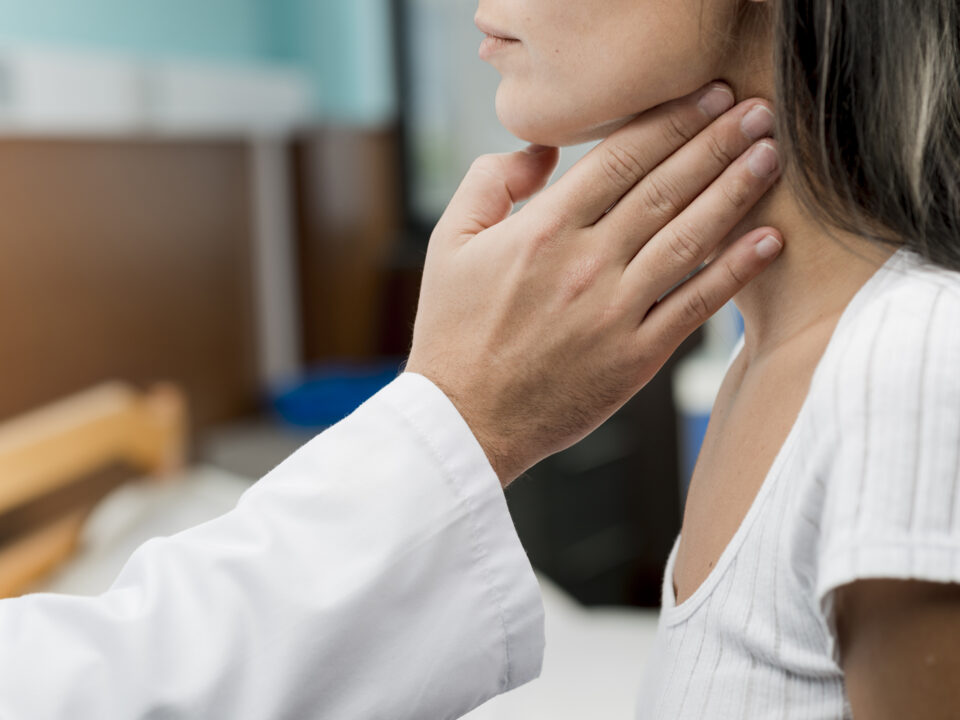
Dry Needling: DN
September 29, 2020
BPB : Brachial Plexus Block
September 30, 2020A soft-tissue foreign body is an object that is stuck under your skin. Examples of foreign bodies include wood splinters, glass, metal, and plastic. Suspected retained foreign bodies are a common reason for emergency department visits.
Foreign bodies embedded in soft tissue can cause allergic reactions, inflammation, or infection. Removal can be difficult and time-consuming, and the potential damage to tissues caused by the procedure must be weighed against the risk posed by a particular foreign body.
Sonography is useful in the detection and localization of radiolucent foreign bodies in soft tissue which can avoid misdiagnosis and tissue damage during a primary emergency evaluation.
Ultrasonography (US) allows detection of a variety of soft-tissue foreign bodies along with the evaluation of their associated soft-tissue complications.
Which ultrasound scanner is used to detect foreign bodies in soft tissue?
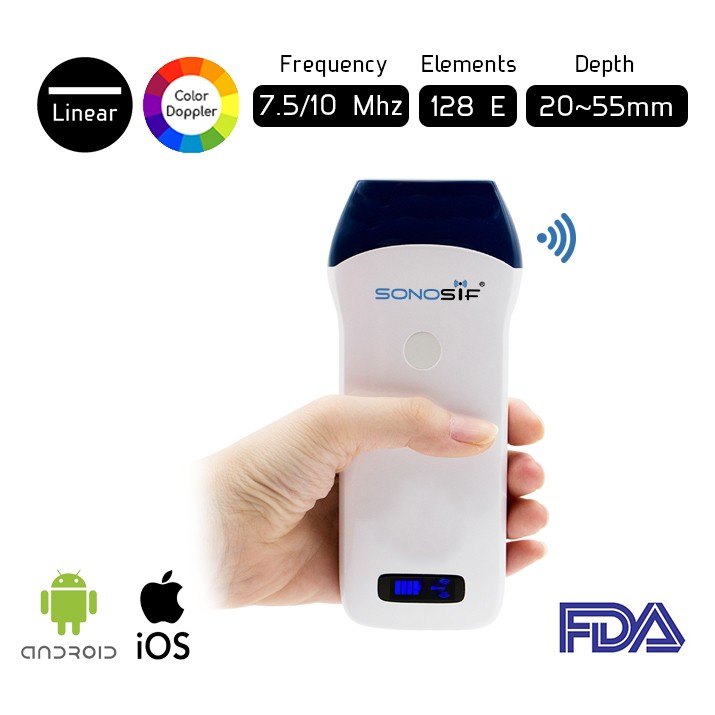
Emergency specialists and orthopedists will need the Wireless Color Doppler Linear Ultrasound Scanner L2CD for this procedure.
A high-frequency (7.5 to 10 Mhz) Wireless Color Doppler Linear Ultrasound Scanner L2CD is optimal for Ultrasound evaluation of soft-tissue foreign bodies.
The linear probe offers improved spatial resolution, achieving anatomic detail of small structures with high accuracy and may identify foreign bodies under 1mm in diameter.
Soft-tissue infection is by far the most common complication of a penetrating foreign body, with nerve injury a distant second.
Ultrasonography allows the identification of foreign bodies in the soft tissues superficial to the intact plantar fascia and plantar tendons. The area of interest is scanned in both the longitudinal and transverse orientations, with attention to the detection of a foreign body and its associated posterior acoustic shadowing or reverberation.
A proper technique requires a slow and meticulous examination, especially in cases of small foreign, where they can be unnoticed. Also, in anatomical areas, like hands and feet, where echogenic structures exist such as sesamoid bones that can result in false positives.
Another aspect to consider is that the echogenicity of foreign bodies also varies according to the orientation of the long axis foreign bodies with respect to the skin. When the foreign bodies are parallel to the skin the visualization is maximum. Moreover, it should be noted that small punctate structures may correspond to bulky foreign bodies if the cutting plane was carried by the short axis, as for example in the case of thorns.
Further advantages of ultrasonography in this particular procedure:
- Localization and easy removal of a foreign body superficial to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon
- Determination of size, shape, and orientation of the foreign body.
- Demonstration of the flexor tenosynovitis which necessitates surgical incision and drainage.
- Examination of the surrounding muscles, tendons, ligaments, and neurovascular structures and assessment of associated injuries.
L2CD is a portable device and readily available imaging modality for superficial soft tissues without the risk of ionizing radiation. It interfaces with Tablet or smartphone and it is IOS and Android compatible.
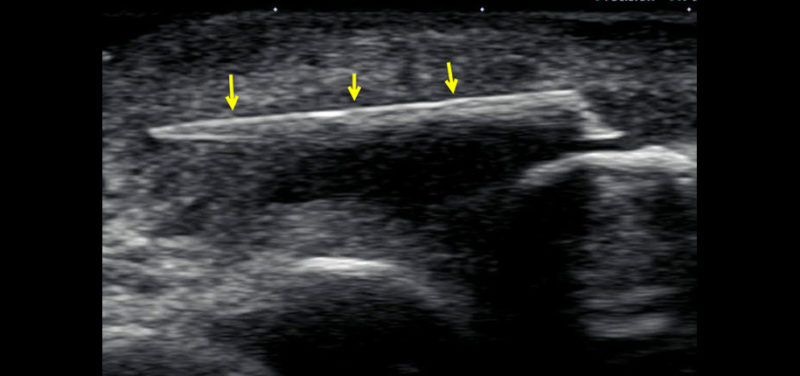
References: Pub Med , Soft- tissue foreign bodies: Diagnosis and removal under ultrasound guidance PDF