Ultrasound-Guided Medial Collateral Ligament
May 8, 2021
Portal Vein Thrombosis_Ultrasound
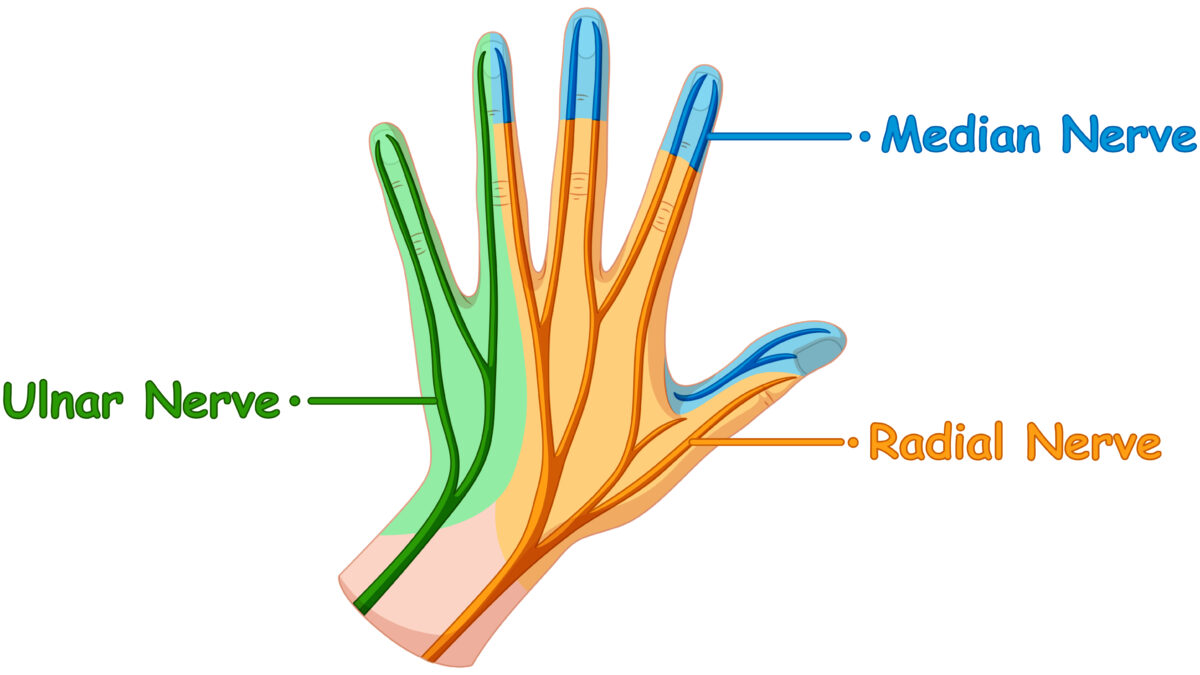
May 23, 2021The median nerve is the forearm’s main nerve. It controls the coarse movements of the hand by supplying the front of the forearm muscles and the muscles of the thenar eminence. “Laborer’s nerve “is another name for it.
It has two roots, one from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus and the other from the medial cord; these embrace the lower portion of the axillary artery, uniting either in front of or lateral to the vessel. It gets its fibers from the sixth, seventh, and eighth cervical nerves, as well as the first thoracic nerve.
After receiving the anterior interosseous and palmar cutaneous branches, the median nerve enters the carpal tunnel and connects to the wrist.
The median nerve (MN) may be affected by various peripheral neuropathies, each of which may be categorized according to its cause, as either an extrinsic (due to entrapment or nerve compression) or an intrinsic (including neurogenic tumors) neuropathy.
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), for example, is caused by a bracelet compression of the median nerve and the most common upper extremity trap neuropathy. If non-surgical care is needed, the treatment can be done by chirurgical or non-surgical methods; a local corticosteroid injector can be used to alleviate pain and tingling.
According to a report on the efficacy of ultrasound-guided carpal tunnel injection, direct needle damage to the median nerve is common, and corticosteroid injectate leakage from the carpal canal triggers problems such as fat tissue atrophy and skin color changes. Thus it is critical to accurately inject the carpal tunnel.
Ultrasound-guided injection (USI) will visually affirm effective injections within the carpal canal, reducing patient discomfort and the chance of median nerve injury.
During the examination of the median nerve at the level of the carpal canal and ulnar nerve, it is strongly advised to use a high-frequency linear ultrasound scanner. As the USB Linear Ultrasound Scanner: 6-15MHz USB-UL3, which has a frequency range of 5 to 12MHz and a scanning mode of B, B+B, B+m with high-resolution imaging for Superfitional applications such as Vascular and Nerve, etc…
A stable ultrasound pulse makes the signal delivery smoother, an amazing image quality leads the medical professional to a straightforward conclusion, and it is simple to bring, thanks to its sealed head and USB connector. When anatomical defects or space-occupying lesions are present, USB-UL3 may also show the source of nerve compression.
References: Median Nerve, The median nerve, Ultrasonography for nerve compression syndromes of the upper extremity, Assessment of Median Nerve Mobility by Ultrasound Dynamic Imaging for Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome,
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SONOSIF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.