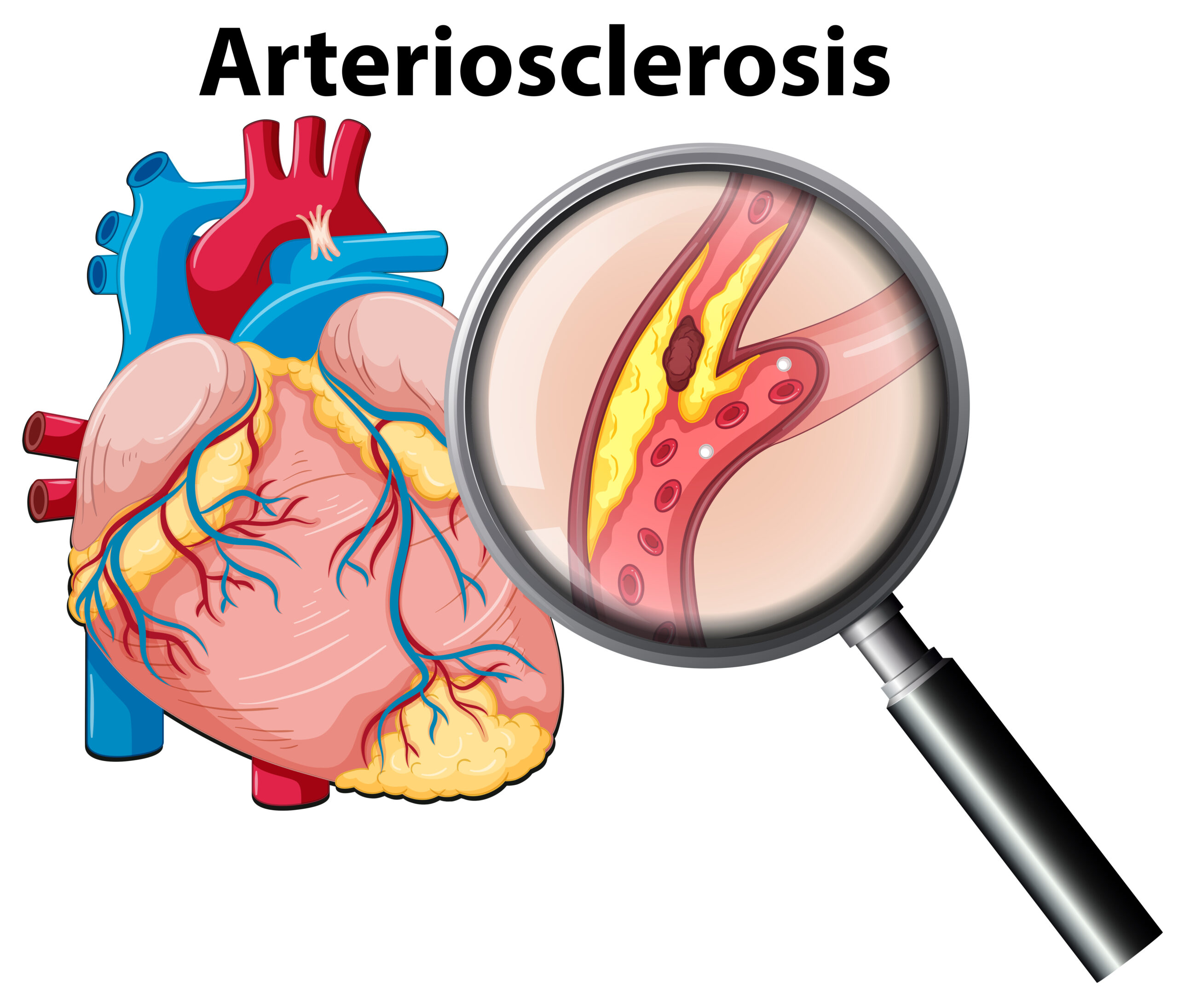
Arteriosclerosis
May 25, 2021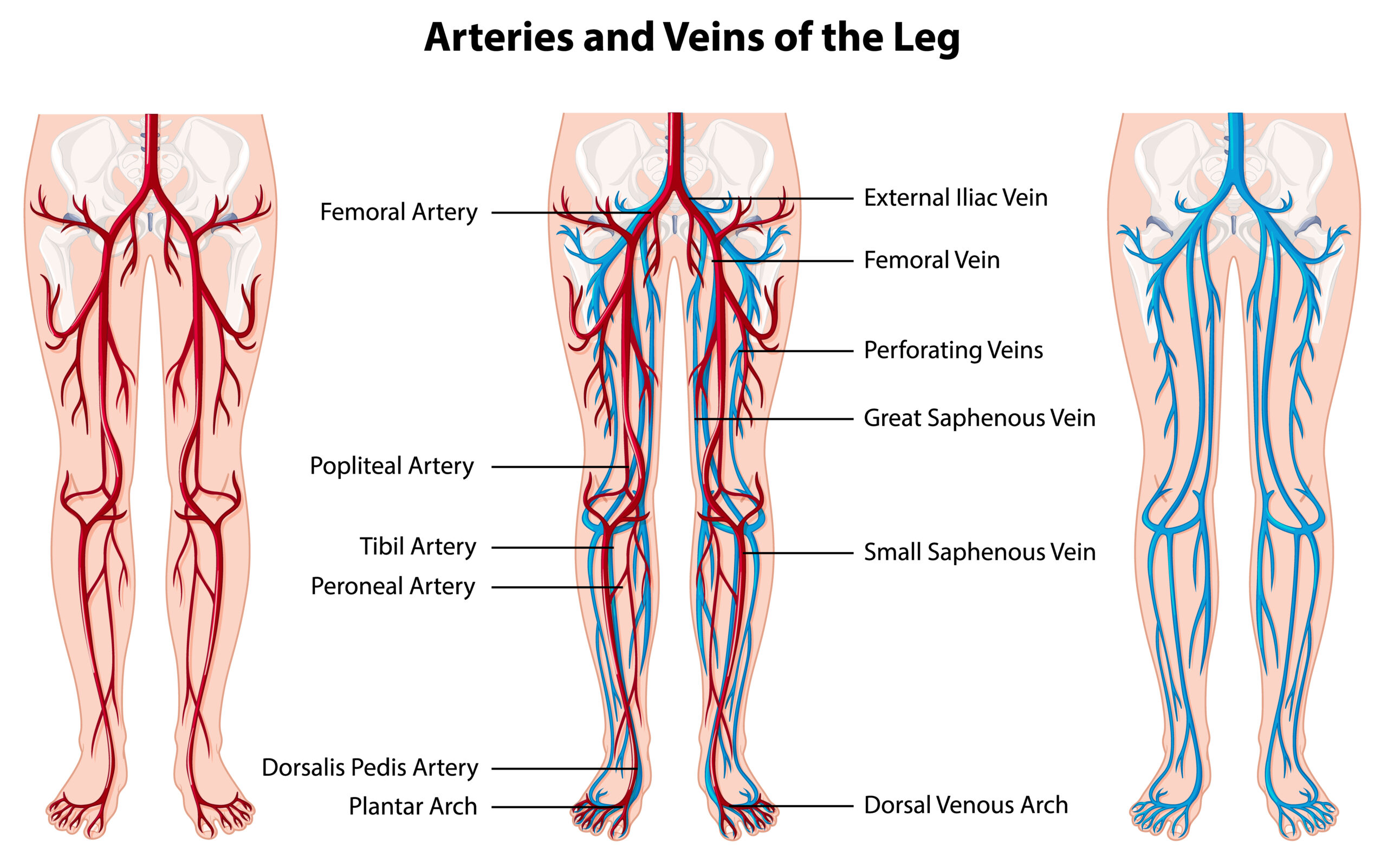
Renal Arteries and Veins Visualization
May 26, 2021The sciatic nerve helps control sensations in the lower body. Sometimes, it is followed by pain when a condition like a herniated disc, degenerative disc disease, or an injury to the lower back compresses the sciatic nerve. This type of nerve pain, aka sciatica, causes radiating back pain that shoots down the buttocks and legs. A block helps relieve these symptoms.
The later is frequently used for anesthesia or analgesia during orthopedic foot surgery. Although anatomical landmarks provide valuable clues to the position of the sciatic nerve, they are only surrogate markers, can vary in patients, and may be difficult to locate in obese patients.
The Ultrasound-guided is a useful diagnostic technique with short examination time that may reduce the risk of femoral artery puncture compared with the landmark-based technique.
So which ultrasound scanner is best for the Subgluteal sciatic nerve block?
The sciatic nerve is imaged approximately at the level of the minor trochanter. It needs to scan at this location using a low-frequency, 5–2 MHz, curved array probe, and a Color Doppler Ultrasound.
The Convex Ultrasound Scanner CC-3.1 helps in diagnosing common conditions, including consolidation, interstitial syndrome, pleural effusions and masses, pneumothorax, and diaphragmatic dysfunction. It offers procedural guidance for various pulmonary procedures, including thoracentesis, chest tube insertion, transthoracic aspiration, and biopsies.
Since it provides color scanned and clear images SONOSIF’s medical Research and Development team always recommend the CC-3.1 to neurologists, general practitioners, Chiropractors, and physical therapists. In which it is useful in many medical specialties such as Pulmonology, emergency, Cardiovascular Medicine, the clinic, outdoor, pregnancy, abdominal diagnosis, and vet inspections.
The physician may use Ultrasound Scanner and inject a dye to identify the pathway of the nerve block needle. Once the position of the needle is confirmed, an anesthetic and steroid solution mixture is injected into the damaged nerves. The physician applies a bandage over the injection site, and the patient is monitored after the procedure.
To sum up, the Subgluteal space, where the sciatic nerve is located, is a well-defined anatomical space and can be identified using ultrasound at the level of the greater trochanter and Ischial tuberosity. The subgluteal space’ is an effective site for a local anesthetic injection or catheter insertion during ultrasound-guided SNB.
References: The sciatic nerve block ,The sciatic nerve block Landmarks and Nerve Stimulator Technique, Ultrasound-guided sciatic nerve block
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SONOSIF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.