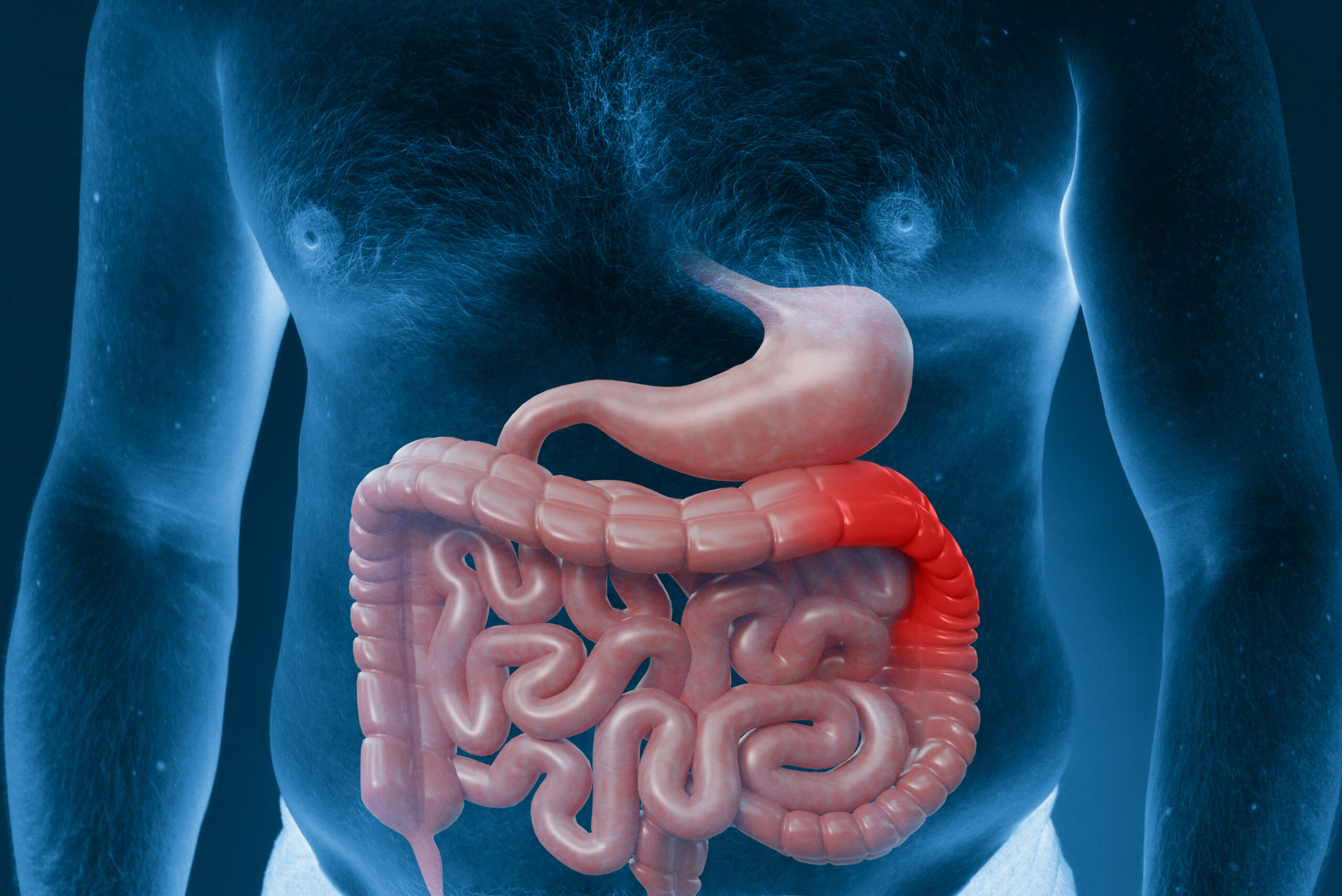
Crohn’s Disease Ultrasound Diagnosis
February 16, 2023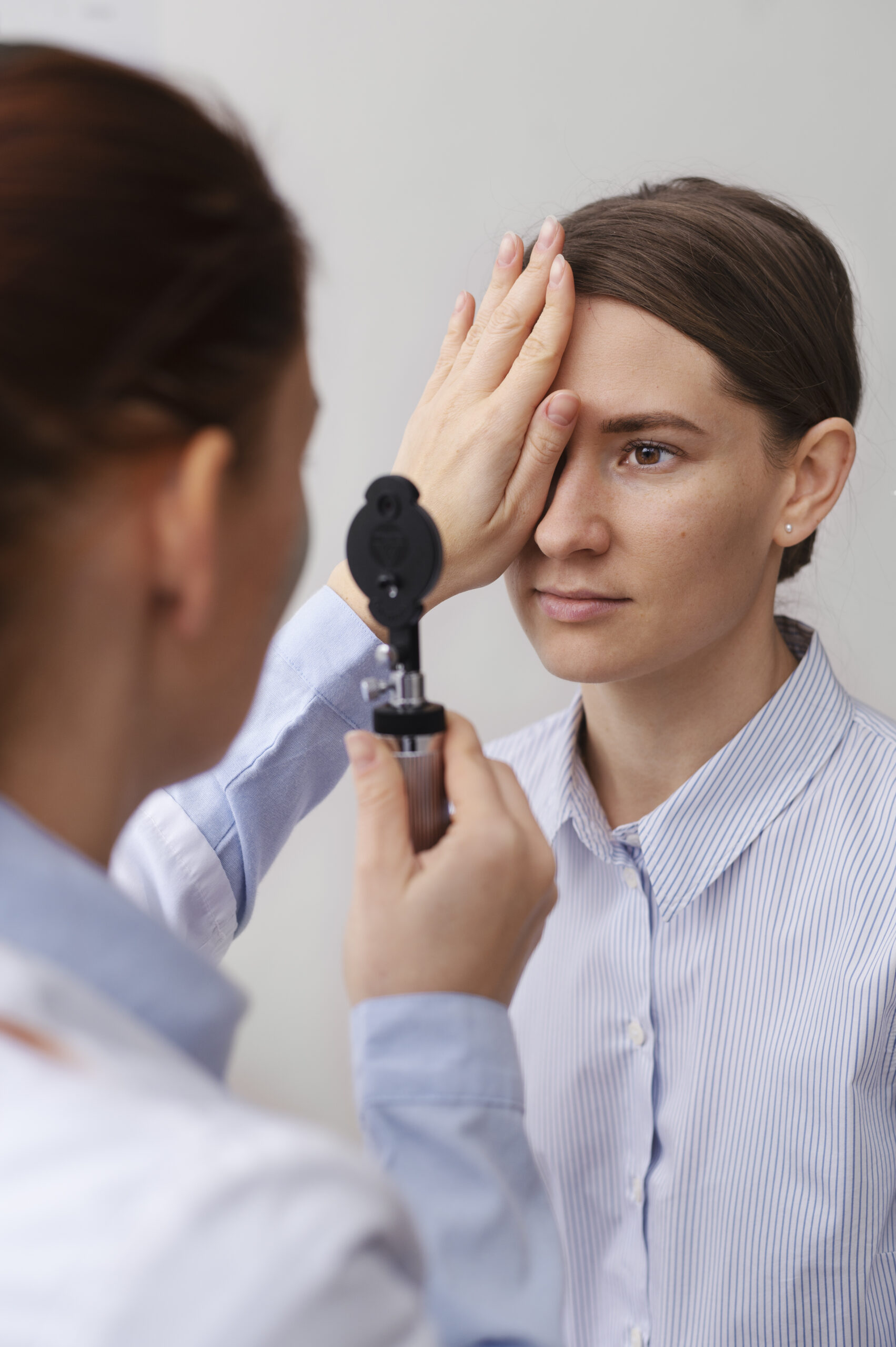
Innovations in Ophthalmology: Unveiling the Potential of High-Frequency Probes
November 15, 2023In the field of anesthesia, resuscitation, and analgesic therapy, medical advancements have brought about significant improvements in patient care. One such advancement is the use of linear ultrasound scanners like the ML1 and MLCD, which have revolutionized these areas of medical practice.
- Enhanced Visualization and Precision:
Linear ultrasound scanners have proven invaluable in anesthesia resuscitation and analgesic therapy by providing enhanced visualization of anatomical structures.
ML1 and MLCD scanners allow anesthesiologists and pain management specialists to accurately locate nerves, blood vessels, and other relevant structures before administering regional anesthesia or performing nerve blocks.
The real-time imaging capabilities of the MLCD scanner enable precise needle guidance during procedures, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall success rates.
By ensuring accurate needle placement, the SIFULTRAS scanners contribute to improved pain management and patient comfort during surgical procedures.
- Efficient Diagnosis and Treatment
In anesthesia resuscitation and analgesic therapy, prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial. ML1 and MLCD scanners aid in the assessment of various conditions, including trauma-related injuries, abdominal pain, and postoperative complications.
These scanners visualize internal organs and guide treatment decisions.
Moreover, linear ultrasound scanners assess analgesic interventions, adjusting dosage or technique to optimize pain relief, ensuring effectiveness.
- Portability and Versatility
ML1 and MLCD scanners are known for their compact size and portability, making them readily available in emergency settings, operating rooms, and intensive care units.
Their versatility allows for a wide range of applications, from vascular access and regional anesthesia to the evaluation of soft tissue injuries. This portability and versatility contribute to increased efficiency, enabling clinicians to promptly respond to patient needs.
The integration of linear ultrasound scanners in anesthesia resuscitation and analgesic therapy has transformed the field, improving patient outcomes and procedural accuracy.
With their enhanced visualization capabilities, efficient diagnosis, and portability, these scanners have become indispensable tools for anesthesiologists and pain management specialists, enhancing patient care and safety in diverse clinical settings.



