VeniPuncture: VP
October 15, 2020
Ultrasound-Guided Paracentesis
October 15, 2020Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
SSUCv3H4sIAAAAAAACA01RwU7DMAz9FcvnwkDcekMwTXCahsRl4uCmbmc1Taok7Zim/jtOt6HdbL+n5+fnM1YUxWB5RrF2jClQEu+wfC6Qa0k+CFksn+YCY6I0Ro7K1c5Q4lbRpb+J7M95jiV+3GnF1ZuV4eE1JFSRsVL4m40q41zc+P8Izj8FUsvOnPIeXRTYMi1r9wp1x8Shv3qYpGZ/KWmsJZc4eUNW8ZfsUT34Pk/bQMNBTJCJQ+5rjkYL3Kx379BYSiCu8VdWhKOkA7SkF0iSCEFiBw1lzxHI1RBP/aDKEablELiP7hHWmhtVlmG9/VroO3Y1K8vB53YDjQ895SzS7/X0SwYXrbgy3hke0kh2RVVWNZnsO/3JPM9/qDZhhrEBAAA=
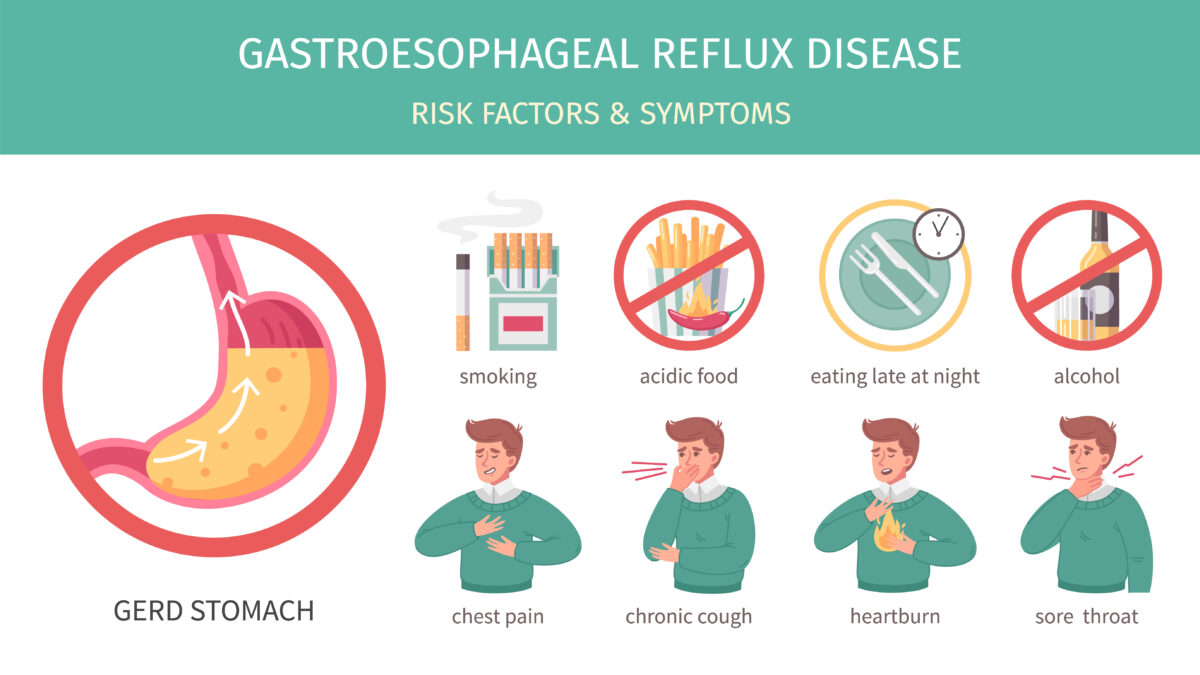
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting the mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of the esophagus. This is called the Heartburn which is a famous problem made by acid reflux, a condition where the acid is forced back up into the esophagus. It creates a burning pain in the lower chest.
Common signs and symptoms of GERD include a burning sensation in the chest (heartburn); usually after eating, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, regurgitation of food or sour liquid, and sensation of a lump in the throat.
Instead of using the long procedure of endoscopy to visualize the esophagus and the stomach, only need the new point-of-care ultrasound application to scan what is inside the patient. We call this gastric ultrasonography or gastric ultrasound or gastric sonography.
Which Ultrasound Scanner is suitable for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
The Convex and Linear Color Doppler Wi-Fi Double Head Ultrasound Scanner CLCD is highly recommended to our gastrologist clients. It is not only non-invasive, readily available, repeatable but also is a fast and highly sensitive technique in the diagnosis of GERD.
The CLCD has two heads. Thus, making it more practical and more affordable than buying two separate single-headed probes. The Linear side of the Doppler allows the practitioner to evaluate the more superficial parts of the body while the Convex part is used for in-depth examinations.
The parts that are situated farthest from the stomach (antrum and body) are better evaluated in a semi-sitting or RLD position. Using a curved array low-frequency transducer from 3.5 to 5 MHz with standard abdominal settings is most useful in adults. And a linear high-frequency transducer can be used with pediatric patients or to get detailed images of the gastric wall, which is 4 to 6 mm thick and has features of five distinct sonographic layers that are best visualized with a high-frequency transducer from 7.5 to 10 MHz in the fasting state.
Sonographic detection of GERD is mainly based on the detection of the returning gastric fluid to the esophagus, so the Doppler technique helps to increase the sensitivity of the mentioned method.
References: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Sonographic Measurement,